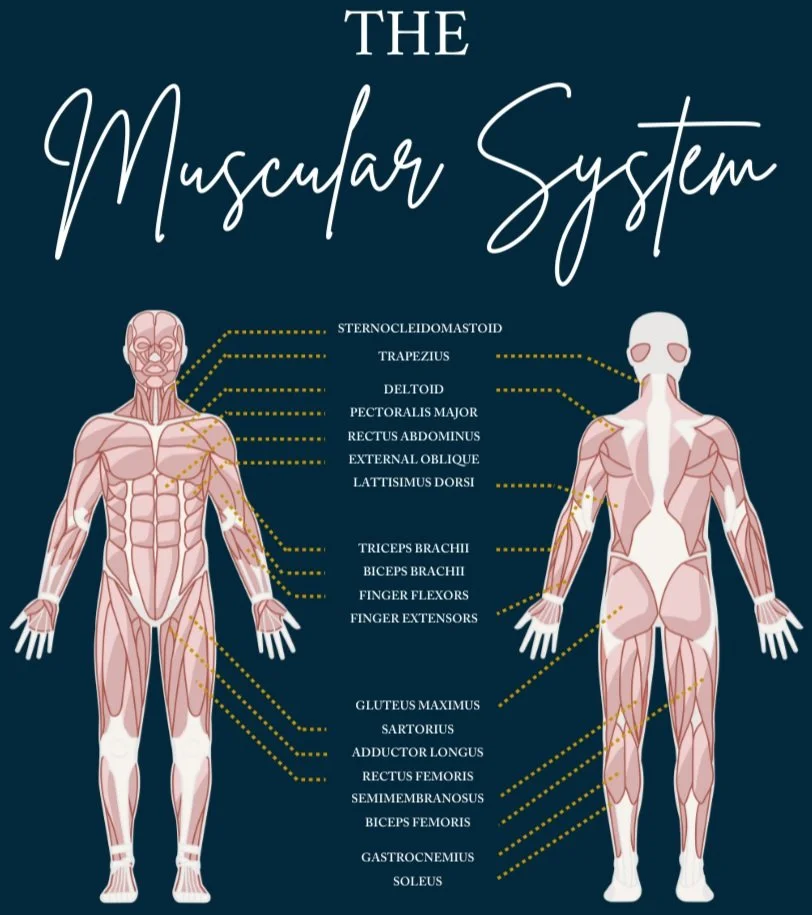
The Muscular System And Common Neuromuscular Conditions
The Function Of The Muscular System
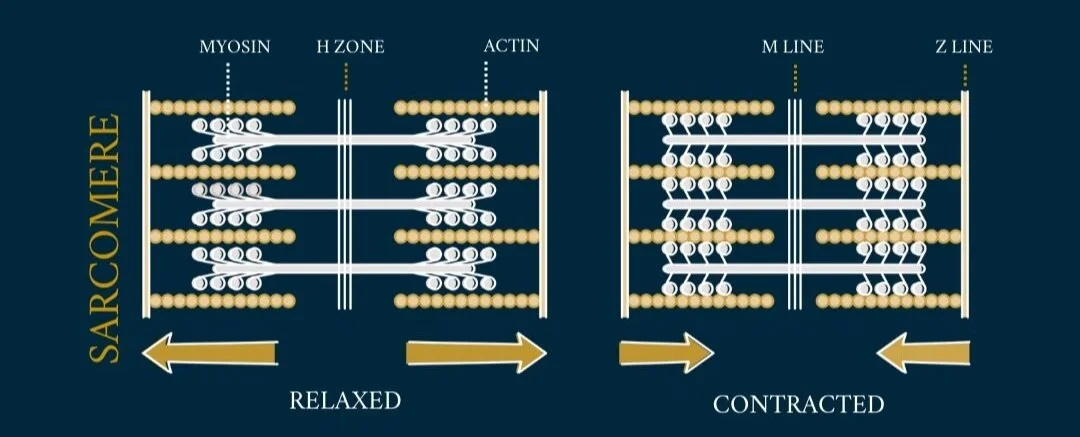
The muscular system is composed of specialized cells called muscle fibers. Their predominant function is contractibility. Muscles, attached to bones or internal organs and blood vessels, are responsible for movement. Nearly all movement in the body is the result of muscle contraction
Types Of Neuromuscular Conditions
Muscular Dystrophy
Is a group of genetic diseases that cause progressive weakness of the body's muscles. Some types of muscular dystrophy will present symptoms in early childhood, while other types will appear in adulthood. Different muscle groups also may be affected depending on the type of muscular dystrophy
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
Is an inherited nerve problem. It causes abnormalities in the nerves that supply your feet, legs, hands, and arms. It affects both your motor and sensory nerves. Motor nerves carry signals from your brain to your muscles, telling them to move. Sensory nerves carry sensations, such as heat, cold, and pain back to your brain. CMT is considered a peripheral neuropathy because it affects nerves outside of your brain and spinal cord
Myopathy
Is a general term referring to any disease that affects the muscles that control voluntary movement in the body. Patients experience muscle weakness due to a dysfunction of the muscle fibers. Some myopathies are genetic and can be passed from parent to child. Others are acquired later in life and can be due to autoimmune disease, known as myositis, metabolic disorders or other causes
How Chiropractic Care Can Help
Chiropractic care may help to allow your nerves to better communicate to your body and muscular system, speak to our friendly team for all the details.
What To Expect At Your First Chiropractic Visit
An initial Chiropractic exam for back pain will typically have three parts: a consultation, case history, and physical examination. Laboratory analysis and X-ray examination may be performed.
Consultation. The patient meets with the chiropractor and provides a brief synopsis of his or her lower back pain, such as:
Duration and frequency of symptoms
Description of the symptoms (e.g. burning, throbbing)
Areas of pain
What makes the pain feel better (e.g. sitting, stretching)
What makes the pain feel worse (e.g. standing, lifting).
Case history. The chiropractor identifies the area(s) of complaint and the nature of the back pain by asking questions and learning more about different areas of the patient's history, including:
Family history
Dietary habits
Past history of other treatments (chiropractic, osteopathic, medical and other)
Occupational history
Psychosocial history
Other areas to probe, often based on responses to above questions
Physical examination. A chiropractor may utilize a variety of methods to determine the spinal segments that require chiropractic treatments, including but not limited to static and motion palpation techniques determining spinal segments that are hypo mobile (restricted in their movement) or fixated. Depending on the results of the above examination, a chiropractor may use additional diagnostic tests, such as:
X-ray to locate subluxations (the altered position of the vertebra)
A device that detects the temperature of the skin in the paraspinal region to identify spinal areas with a significant temperature variance that requires manipulation.
Chiropractors are trained in a variety of methods to assess the underlying cause of the problem, including:
Evaluation and management services. Chiropractors are trained in examining the joints, bones, muscles and tendons of the spine, head, extremities and other areas of the body with the purpose of noting any misalignment, tenderness, asymmetry, defects or other problems.
Neurologic and other common physical examination procedures. Chiropractors are trained to perform a variety of neurologic tests (nerve root compression/tension, motor strength, coordination, deep tendon and pathological reflexes, etc.) and are skilled in performing orthopedic, cardiovascular and many other common examinations.
Specialised assessment. Chiropractors are trained to assess range of motion, stability, muscle strength, muscle tone and other assessments with the lower back.
Common diagnostic studies. Chiropractors are trained in use of diagnostic studies and tools such as radiography (X-rays), laboratory diagnostics and neurodiagnostics.
References
2. https://www.cedars-sinai.org/health-library/diseases-and-conditions/n/neuromuscular-disorders.html
3. https://www.mda.org.nz/Neuromuscular-Conditions
4. https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/neuromuscular-disorders
5. https://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/muscular/
6. https://www.innerbody.com/image/musfov.html
7. https://www.uc.edu/content/dam/uc/ce/images/OLLI/Page%20Content/Muscular%20System%20s.pdf
8. https://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/muscular-system#1
9. https://www.visiblebody.com/learn/muscular/muscular-overview
11. https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/the-musculoskeletal-system
12. https://wyldchiropractic.co.nz/wyldlife/massage-benefits