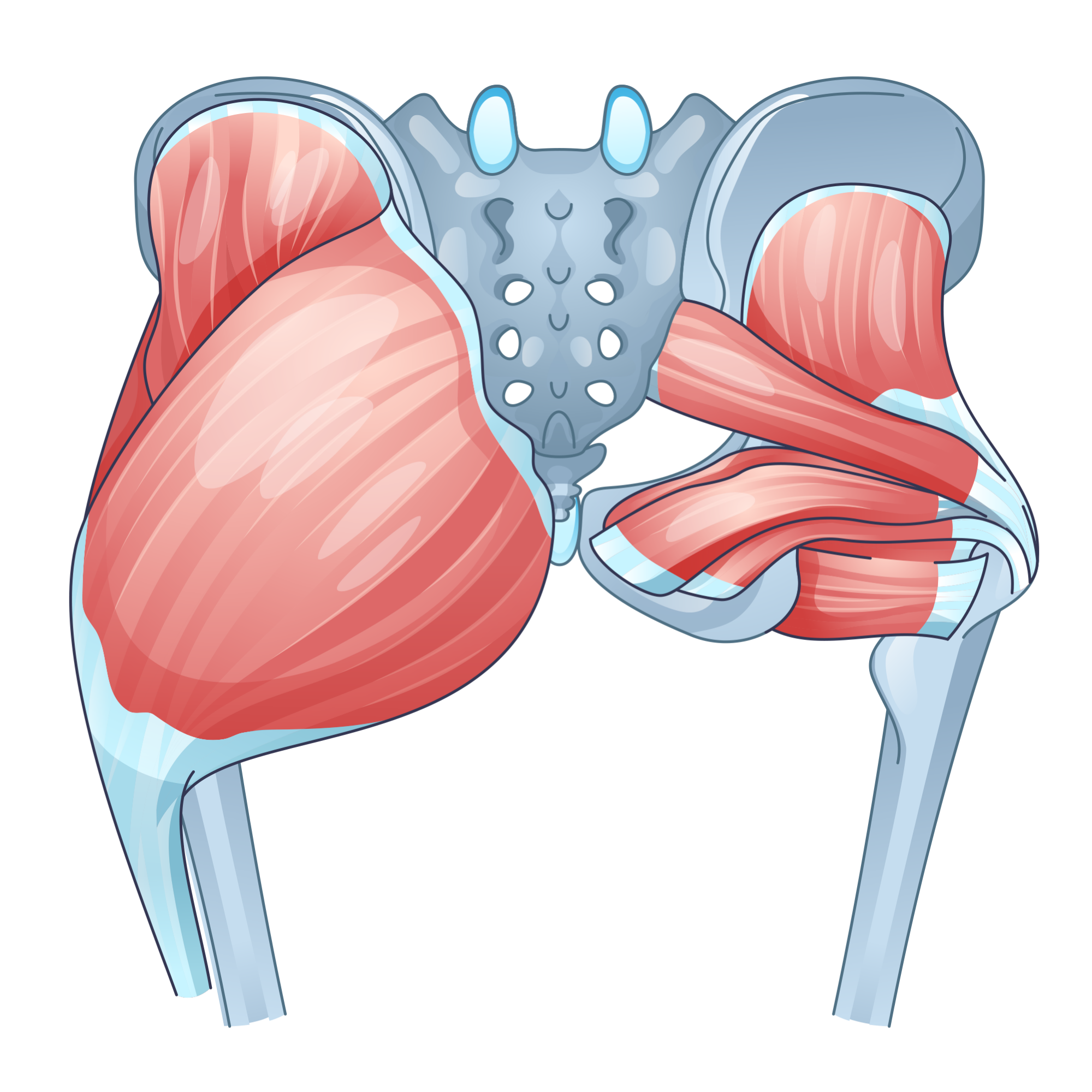
Snapping Hip Syndrome
A snapping hip is a condition in which you hear a clicking sound from your hip from any activity that involves the hip joint such as walking or getting up from a chair. The snapping sound is heard because the muscles/tendons that surround the hip joint become taught and move over a bony protrusion in the hip.
Usually a snapping hip is painless and harmless, but in some cases this can lead to bursitis which is a painful swelling due to the hip joint being filled with fluid. Snapping hip is common in young athletes as the muscles that surround the hip tend to get tight during growth spurts and activities that frequently involve engaging the hip joint such as dancing.
The snapping can occur in different areas of the hip:
Outside of the hip
This is the most common area where a clicking sound is heard. This is where the iliotibial (IT) band passes over the greater trochanter. In other words when the hip is straight the IT band usually sits behind the greater trochanter, but when we bend the hip this band usually slides across the greater trochanter.
If the IT band is tight the movement of it across the greater trochanter can create that snap sound. Over time the bursa which is a fluid-filled sac that allows the muscle to move over the bone smoothly can become inflamed resulting in hip bursitis.
Front of the hip
This is usually caused due to the snapping of the rectus femoris tendon. This tendon usually moves across the head of the thigh bone when bent, and moves to the side when the hip is flexed. When taught it can create a snapping sound.
Back of the hip
The back of the hip can involve the hamstring tendon. The hamstring tendon attaches to the sitting bones called the ischial tuberosity. When taught it can rub against the ischial tuberosity resulting in snapping. This one is not usually as common as the other forms of hip snapping.
Another cause of hip snapping is when the protective cover (also known as the labrum) of where the thigh bone attaches to the hip tears and can cause the hip to pop or even lock up. However a torn labrum usually results in a deep ache which is uncommon with a snapping hip.
Remedies:
Reduce the level of activity you are doing.
Reduce repetitive movement of the hip.
Stretching the Iliotibial band, Hamstrings and piriformis muscle.
Seeing a chiropractor who will ensure the spine is aligned to take the pressure of the surrounding muscles and hip joint. The chiropractor may also give an exercise regime to speed up the recovery process.
What To Expect At Your First Chiropractic Visit
An initial Chiropractic exam for back pain will typically have three parts: a consultation, case history, and physical examination. Laboratory analysis and X-ray examination may be performed.
Consultation. The patient meets with the chiropractor and provides a brief synopsis of his or her lower back pain, such as:
Duration and frequency of symptoms
Description of the symptoms (e.g. burning, throbbing)
Areas of pain
What makes the pain feel better (e.g. sitting, stretching)
What makes the pain feel worse (e.g. standing, lifting).
Case history. The chiropractor identifies the area(s) of complaint and the nature of the back pain by asking questions and learning more about different areas of the patient's history, including:
Family history
Dietary habits
Past history of other treatments (chiropractic, osteopathic, medical and other)
Occupational history
Psychosocial history
Other areas to probe, often based on responses to above questions
Physical examination. A chiropractor may utilize a variety of methods to determine the spinal segments that require chiropractic treatments, including but not limited to static and motion palpation techniques determining spinal segments that are hypo mobile (restricted in their movement) or fixated. Depending on the results of the above examination, a chiropractor may use additional diagnostic tests, such as:
X-ray to locate subluxations (the altered position of the vertebra)
A device that detects the temperature of the skin in the paraspinal region to identify spinal areas with a significant temperature variance that requires manipulation.
Chiropractors are trained in a variety of methods to assess the underlying cause of the problem, including:
Evaluation and management services. Chiropractors are trained in examining the joints, bones, muscles and tendons of the spine, head, extremities and other areas of the body with the purpose of noting any misalignment, tenderness, asymmetry, defects or other problems.
Neurologic and other common physical examination procedures. Chiropractors are trained to perform a variety of neurologic tests (nerve root compression/tension, motor strength, coordination, deep tendon and pathological reflexes, etc.) and are skilled in performing orthopedic, cardiovascular and many other common examinations.
Specialised assessment. Chiropractors are trained to assess range of motion, stability, muscle strength, muscle tone and other assessments with the lower back.
Common diagnostic studies. Chiropractors are trained in use of diagnostic studies and tools such as radiography (X-rays), laboratory diagnostics and neurodiagnostics.
References:
https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/snapping-hip/
https://www.aurorahealthcare.org/services/sports-health/conditions/snapping-hip-syndrome
https://myhealth.alberta.ca/Health/aftercareinformation/pages/conditions.aspx?hwid=bo1646
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448200/